Share
Diagonal Integration
What is Diagonal Integration?
Diagonal integration is the process by which firms use technology to build platforms to get close to their targeted customers. Diagonal Integration is radically different from vertical and horizontal forms of integration.
For eons, firms have integrated horizontally and vertically. They have even diversified their operations. Today, driven by digitalisation and the need to get closer to consumers, Diagonal Integration is increasingly, the new ‘best practice’.
Diagonal Integration is the new “best practice” for competitiveness
Diagonal integration is a term coined by Dr. Auliana Poon, Managing Director of Leve Global, in her book, Tourism, Technology and Competitive Strategies in 1993. It explains the process by which firms use information technology to get closer to their customers and to systematically combine a range of services required by their carefully-identified target clientele. This nis entirely different from selling standardized goods to a supermarket of clients. For example, American Express produces a range of services – travel, insurance, real estate, financial services, investment services – to their carefully-targeted clients.
Integrate Diagonally for Best Productivity and Most Profits
Firms diagonally integrate for best productivity and most profits. As they move into new activities, there are tremendous systems gains, synergies and scope economies to be had from integration. Diagonal integration is a key tool for controlling the process of value creation and will continue to blur the boundaries among industry players.
Competition in the new tourism will not be dominated by full capacity utilisation, cost cutting, over-production, price-cutting and mark-downs. Diagonal integration underlies the platform economy.
The purpose of diagonal integration is not to produce a single service and market it to a supermarket of clients. Rather, the objective is to produce a range of services and to sell them to a target group of consumers. The consumers targeted are expected to simultaneously consume these services at regular intervals over their lifetime (for example, travel + insurance + credit + holiday + personal banking + entertainment + Internet + Radio + TV + Music).
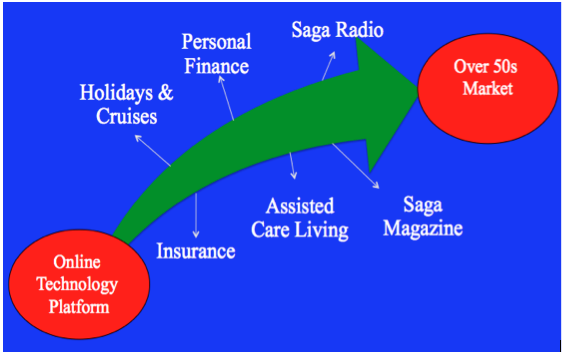
Diagonal Integration Underpins the Platform Economy
Firms such as Airbnb, Amazon and Google are masters of diagonal integration. They use information technology, in this case the Internet, to tightly coordinate a range of related services to their target market.
For example, we all know that Google isn’t just a search engine provider. Their main objective is to ensure their market has an overall positive experience. Google offers search engine services, targeted advertising services, video search (YouTube), image search, Google Drive services, Google App solutions such as word processing, spreadsheet, presentation and form solutions. Google offers cloud storage, Google Store, Chrome browser, Google Classroom, Gmail, Google Maps, Google Translate and much more. All of these services are tightly related to the overall search experience of their clients. None of what Google does today would be possible without the application of information technology. This is diagonal integration at its best.
Technology is Key for Diagonal Integration
Diagonal integration needs three ingredients for it to work: targeted customers, closely-related products, and technology. While they are all important it is technology that truly empowers firms to integrate diagonally. The dawn of the internet has paved the way for diagonal integration. And the platform economy is diagonal integration in action for the most part. Consider that many platforms such as Amazon, Airbnb, TripAdvisor, Expedia, etc. use their internet-based platforms to reach a targeted group of customers ((e.g. travellers) to offer tightly-related products/services. Expedia for example, offers flights, hotel accommodation, and car rental services on their platform. Without the technology, it would have been challenging for service providers like Expedia to reach their target markets and to offer the range of services in a one-stop shop.
Technology is the vehicle that delivers diagonal integration. In fact, diagonal integration has paved the way for the Amazons, Netflix, Airbnbs and Ubers of this world. In her book, Tourism Technology and Competitive Strategies (polished in 1988, 20 years before), Poon asserts that “with diagonal integration ownership may not be necessary. In fact, diagonal integration could be achieved through strategic alliances and information partnerships”. This is why the largest accommodation provider in the world owns no hotels (Airbnb), the largest taxi company owns no taxis (Uber) and the largest retail outlet owns no stores (Amazon).

Diagonally Integrate to Get Close to Your Customers
Firms that are adopting diagonal integration to build their platform economies are winning. This is because of the sheer synergies, scale, scope and network possibilities created. In other words, the benefits of integrating activities are greater than providing each activity separately, especially when the same customers are involved.
Diagonal integration is facilitated by new information technologies. It is the process by which firms use information technologies to logically combine services (for example, financial services and travel agencies) for best productivity and most profits. One of the key attractions to firms in diagonally integrating is the lower costs of production that comes with it. This is made possible through the synergies, systems gains and scope economies that firms reap when they use an IT platform to integrate diagonally.

